What It Is:
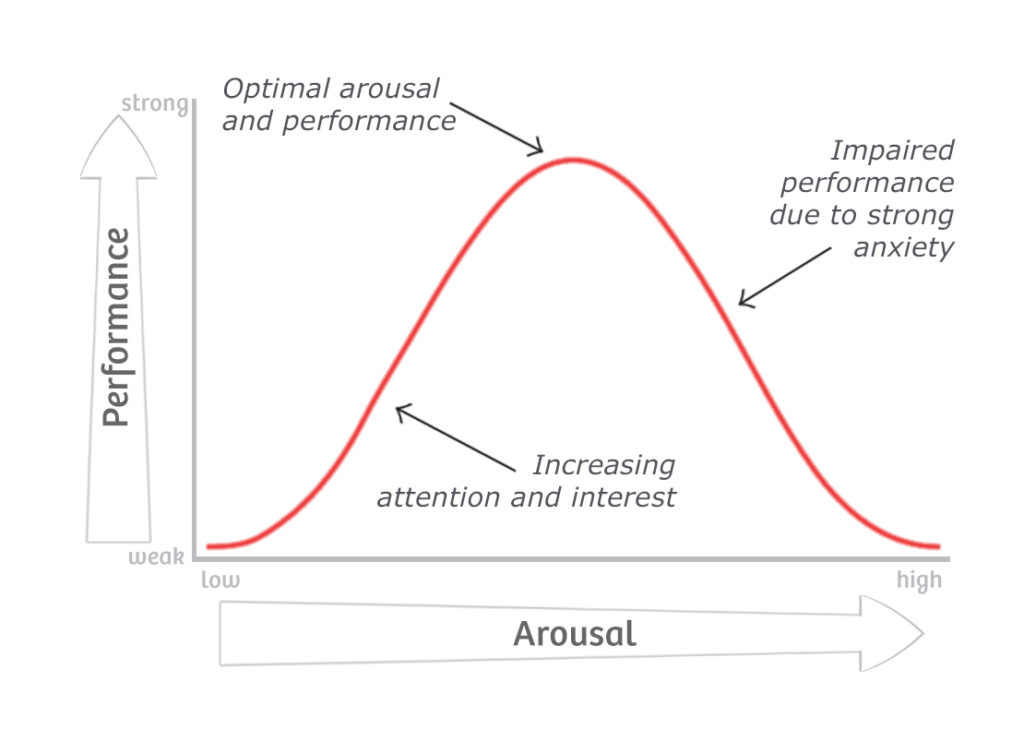
The Yerkes-Dodson Law is a psychological principle that describes the relationship between arousal (or stress) and performance. The law suggests that there is an optimal level of arousal for performance on a task, and that too little or too much arousal can lead to decreased performance.
Key Points:
- Optimal Arousal: The Yerkes-Dodson Law proposes that there is an optimal level of arousal or stress for peak performance. This optimal level is different for different tasks and individuals.
- Inverted U-Shaped Curve: The relationship between arousal and performance is often represented by an inverted U-shaped curve. Performance improves with increased arousal, but only up to a certain point, after which further arousal leads to a decline in performance.
- Individual Differences: The optimal level of arousal varies among individuals, and what may be optimal for one person or task may not be optimal for another.
Hebbian Version: There is no widely recognized “Hebbian version” of the Yerkes-Dodson Law. However, the Hebbian learning rule, proposed by psychologist Donald Hebb, is a neurobiological principle that states “cells that fire together wire together.” This rule is not directly related to the Yerkes-Dodson Law but pertains to the synaptic strengthening between neurons based on their simultaneous activity.
How to Use It:
Using Yerkes-Dodson Law in Agile Coaching:
- Understanding Team Stress Levels:
- Assess the stress levels within the team. Understand that a certain level of stress can enhance performance, but excessive stress can lead to burnout and decreased productivity.
- Tailoring Workloads:
- Consider the nature of tasks and projects assigned to the team. Tailor workloads to ensure that they are challenging enough to keep the team engaged but not so overwhelming that it leads to excessive stress.
- Recognizing Individual Differences:
- Recognize that individuals within the team may have different optimal levels of arousal. Some team members may thrive in high-pressure situations, while others may perform better in a more relaxed environment.
- Promoting a Positive Work Environment:
- Foster a positive work environment that minimizes unnecessary stressors. Encourage open communication, provide support, and address any factors that may contribute to excessive stress within the team.
The Yerkes-Dodson Law is a valuable concept for understanding the relationship between stress and performance. Agile coaches can use this knowledge to optimize team performance and create an environment conducive to both productivity and well-being.
References:
- Original Research Papers:
- The Yerkes-Dodson Law was first introduced by psychologists Robert M. Yerkes and John Dillingham Dodson in a series of studies published in the early 20th century. Accessing the original research papers can provide a deeper understanding of their findings.
- Yerkes and Dodson, Hebbian – Diamond DM, et al. (2007). “The Temporal Dynamics Model of Emotional Memory Processing: A Synthesis on the Neurobiological Basis of Stress-Induced Amnesia, Flashbulb and Traumatic Memories, and the Yerkes-Dodson Law”.
- The Yerkes-Dodson Law was first introduced by psychologists Robert M. Yerkes and John Dillingham Dodson in a series of studies published in the early 20th century. Accessing the original research papers can provide a deeper understanding of their findings.
- Psychological Journals:
- Explore psychology journals for articles and research papers that discuss the Yerkes-Dodson Law and its applications in various contexts.
- Books on Performance Psychology:
- Books on performance psychology often delve into the Yerkes-Dodson Law. Look for resources that provide practical insights into applying the law in work and performance settings.
Visit the Agile Coach’s Toolkit for more definitions, models, theorems and stuff.