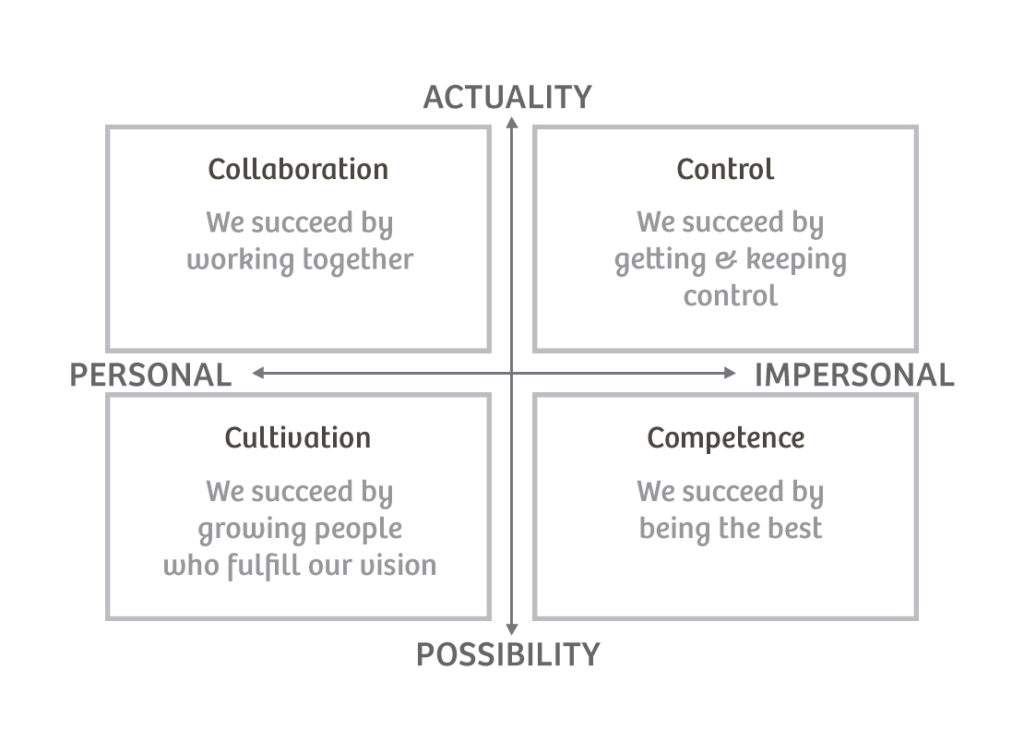
What It Is:
The Schneider Culture Model was developed by William Schneider, an organizational psychologist and founder of the consulting firm William Schneider & Associates. This model is designed to help organizations understand their culture and align it with their strategic goals. It categorizes organizational cultures into distinct quadrants based on two dimensions: people focus vs. task focus and flexibility vs. stability.
Key Dimensions of the Schneider Culture Model:
- People Focus (Personal) vs. Task Focus (Impersonal):
- This dimension assesses whether the organization places a greater emphasis on people and relationships or on tasks and results.
- Flexibility (Possibility) vs. Stability (Actuality):
- This dimension evaluates the organization’s preference for adaptability, innovation, and flexibility versus stability, structure, and order.
Four Culture Quadrants:
- Collaboration Culture (People-Focused & Flexible):
- Emphasizes cooperation, teamwork, and a dynamic, flexible environment. People in this culture value relationships and innovation.
- Control Culture (Task-Focused & Stable):
- Prioritizes efficiency, structure, and stability. Control cultures are task-oriented, with a focus on precision and order.
- Competence Culture (Task-Focused & Flexible):
- Values achievement, innovation, and excellence. It combines a focus on tasks with a willingness to adapt to change.
- Cultivation Culture (People-Focused & Stable):
- Prioritizes relationships, trust, and a stable work environment. It’s a people-oriented culture with a preference for consistency.
How to Use It:
Using Schneider Culture Model in Agile Coaching:
- Understanding Team Dynamics:
- Assess the existing culture within the Agile software delivery team. Identify whether it aligns more with a collaboration, control, competence, or cultivation culture.
- Aligning Culture with Agile Values:
- Explore how the current culture aligns with Agile principles and values. Identify areas where adjustments can be made to better support Agile practices and mindset.
- Facilitating Cultural Change:
- If needed, guide the team in transitioning toward a culture that better supports Agile methodologies. This might involve fostering collaboration, encouraging adaptability, or emphasizing competence and excellence.
- Customizing Agile Practices:
- Tailor Agile practices to fit the existing culture. For example, in a control culture, emphasize structured ceremonies and clear processes, while in a collaboration culture, focus on teamwork, communication, and flexibility.
Understanding the Schneider Culture Model can assist Agile coaches in navigating organizational dynamics and promoting a culture that supports Agile principles and practices. Tailoring Agile approaches to align with the existing organizational culture enhances the likelihood of successful Agile adoption.
References:
- Books by William Schneider:
- William Schneider has written books on organizational culture, including “The Reengineering Alternative: A Plan for Making Your Current Culture Work” and “The Reengineering Alternative: A Plan for Making Your Current Culture Work.”
- Consulting and Training Programs:
- Explore consulting firms or training programs that specialize in organizational culture and change. These programs may provide insights into applying the Schneider Culture Model.
- Organizational Development Journals:
- Look for articles and publications in organizational development journals that discuss the Schneider Culture Model. Academic and professional journals may offer in-depth analyses and case studies.
Visit the Agile Coach’s Toolkit for more definitions, models, theorems and stuff.