What It Is:
Attributed to Ralph D. Stacey
The Stacey Matrix is a management tool developed by Ralph Stacey, a British organizational theorist and Professor of Management at the Business School of Hertfordshire University. The matrix helps in understanding and categorizing complex situations and problems within organizations.
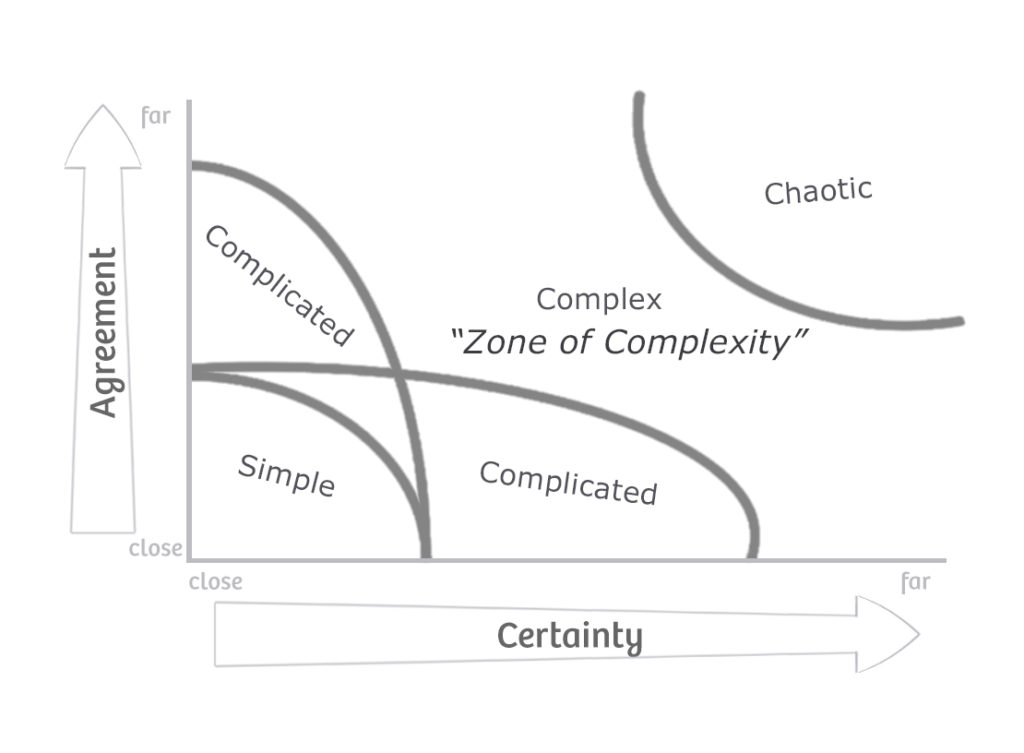
Stacey Matrix:
- Simple (Clear-Cut):
- Characteristics: Well-defined problems with clear cause-and-effect relationships. There is agreement on goals and means.
- Leadership Approach: Directive leadership and standard procedures work well.
- Complicated (Knowable):
- Characteristics: There is a clear relationship between cause and effect, but it might require analysis or expertise to understand. Solutions are available but not immediately obvious.
- Leadership Approach: Expertise and analysis are crucial. Consultative leadership and structured approaches work well.
- Complex (Unpredictable):
- Characteristics: No clear cause-and-effect relationship, and outcomes are uncertain. The system is adaptive and influenced by various factors.
- Leadership Approach: Adaptive and collaborative leadership is required. Experimentation and learning through feedback are essential.
- Chaotic (No Discernible Order):
- Characteristics: Highly unpredictable and turbulent situations where cause and effect are unclear. There is a need for rapid action, and experimentation is crucial.
- Leadership Approach: Crisis management, rapid decision-making, and flexible, responsive actions are required.
- Anarchical (Not Applicable):
- Characteristics: The system is in a state of constant change with no clear cause-and-effect relationships. It may be in the process of disintegration or reorganization.
- Leadership Approach: Facilitation and enabling rather than directing. The emphasis is on allowing self-organization.
How to Use It:
Using Stacey Matrix in Agile Coaching:
- Problem Diagnosis:
- Use the Stacey Matrix to diagnose the nature of the challenges or problems the Agile software delivery team is facing. Determine whether the situation is simple, complicated, complex, chaotic, or anarchical.
- Adaptation of Agile Practices:
- Tailor Agile practices and methodologies based on the nature of the problem. For simple or complicated situations, standard Agile practices may suffice. For complex situations, emphasize adaptive practices, experimentation, and learning.
- Leadership Style:
- Adjust leadership styles based on the quadrant in which the team’s challenges fall. For complex situations, adopt a more collaborative and adaptive leadership approach. In chaotic situations, focus on rapid decision-making and crisis management.
- Facilitation and Feedback:
- In complex situations, facilitate collaborative problem-solving and encourage regular feedback loops. The Stacey Matrix can guide the team in understanding the level of complexity and the need for adaptive approaches.
Understanding the Stacey Matrix allows Agile coaches to navigate and address challenges in a way that aligns with the complexity of the situation. It provides a framework for choosing appropriate approaches and adapting Agile practices based on the specific nature of the problems at hand.
References:
- Books and Publications by Ralph Stacey:
- Ralph Stacey has written extensively on complexity and management. His publications, including books like “Complexity and Organizational Reality,” provide in-depth insights into the Stacey Matrix.
- Academic Journals:
- Explore academic journals in the fields of organizational management and complexity theory. Articles and papers may delve into the application of the Stacey Matrix in various contexts.
Visit the Agile Coach’s Toolkit for more definitions, models, theorems and stuff.