What It Is:
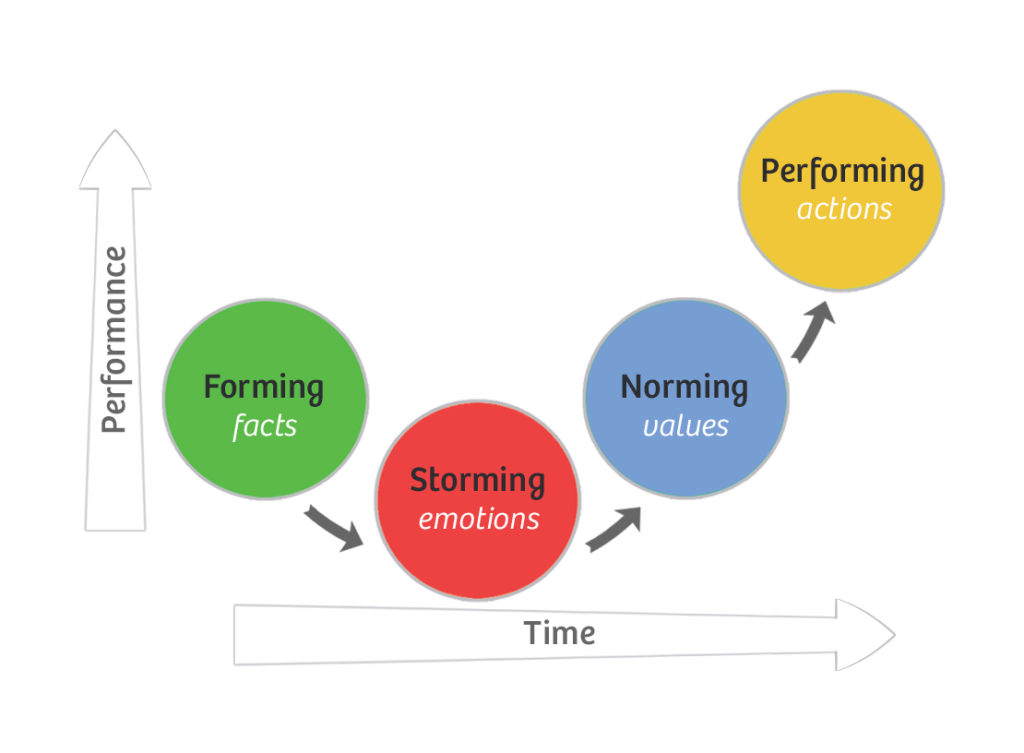
The Tuckman Model of Group Development, also known as Forming-Storming-Norming-Performing, was developed by psychologist Bruce Tuckman. The model describes the stages that groups go through as they form, establish roles and norms, address conflicts, and become cohesive and productive.
Stages of the Tuckman Model:
- Forming: The team comes together, and members get to know each other. They explore the boundaries of acceptable behavior and the scope of the project.
- Storming: Conflict and tension emerge as team members start expressing their individuality. This stage involves negotiating roles, responsibilities, and expectations.
- Norming: The team establishes norms, resolves conflicts, and develops a sense of unity. Roles and responsibilities become clearer, and team members start collaborating more effectively.
- Performing: The team reaches a state of high performance. Members work together smoothly, and the focus is on achieving the team’s goals.
- Adjourning (or Mourning): In some versions of the model, a fifth stage, adjourning, is added to represent the team’s dissolution after completing its goals.
How to Use It:
Using the Tuckman Model in Agile Coaching:
- Understanding Team Dynamics:
- Use the Tuckman Model to help teams understand the natural progression of group development. This understanding can foster patience and resilience during challenging stages.
- Facilitating Team Building:
- Tailor team-building activities based on the current stage of development. For example, during the forming stage, focus on ice-breaking activities, and during storming, facilitate discussions to address conflicts constructively.
- Conflict Resolution:
- Acknowledge that conflict is a natural part of team development. Help the team navigate through storming by facilitating open communication and providing tools for resolving conflicts.
- Establishing Team Norms:
- Emphasize the importance of establishing team norms during the norming stage. Encourage the team to collaboratively define expectations, communication protocols, and working agreements.
- Celebrating Achievements:
- Recognize and celebrate achievements as the team progresses to the performing stage. Reinforce positive behaviors and accomplishments to enhance team morale.
The Tuckman Model is a valuable framework for understanding and addressing the dynamics of group development. Agile coaches can use it as a tool to guide teams through challenges and promote effective collaboration.
References:
- Original Publication:
- The original paper by Bruce Tuckman, titled “Developmental Sequence in Small Groups,” published in 1965, outlines the stages of group development.
- Subsequent Works:
- Explore subsequent works and updates by Tuckman and other researchers that may provide additional insights into the model.
- Agile Literature:
- Agile literature often references the Tuckman Model in the context of team dynamics and development. Agile and Scrum books may provide practical applications of the model in software development teams.
- Team Development Workshops:
- Participate in or conduct workshops on team development that incorporate the Tuckman Model. Practical activities can enhance understanding and application.
Visit the Agile Coach’s Toolkit for more definitions, models, theorems and stuff.