What It Is:
Gerald Weinberg, in his book “The Secrets of Consulting”, introduced the concept of the “Law of Raspberry Jam.” This law states, “The wider you spread it, the thinner it gets.” It reflects the effects of project switching or multitasking on individual and team productivity.
Effects of Project Switching (Law of Raspberry Jam):
- Reduced Productivity:
- Project switching or multitasking can lead to reduced productivity. When individuals are constantly shifting their attention between multiple projects, it takes time to refocus on each task, leading to inefficiencies.
- Decreased Quality of Work:
- Rapidly switching between projects can compromise the quality of work. Individuals may not have the time or mental bandwidth to deeply engage with each task, potentially resulting in errors or suboptimal outcomes.
- Increased Stress and Fatigue:
- Constant project switching can contribute to increased stress and mental fatigue. The cognitive load of managing multiple tasks simultaneously can be overwhelming, impacting overall well-being.
- Extended Time to Completion:
- While it might seem that working on multiple projects simultaneously could expedite completion, the opposite often occurs. Constant context-switching introduces overhead, leading to a longer time to complete each task.
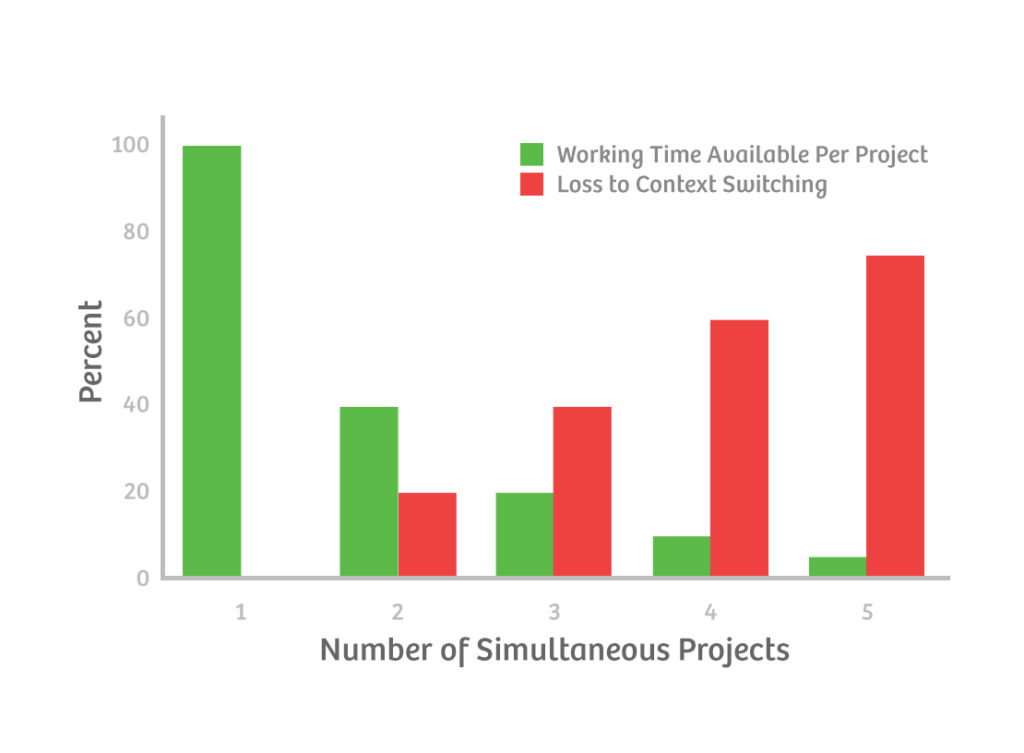
Consider the following chart:
How to Use It:
Using the Concept in Agile Coaching:
- Advocating for Focus:
- Encourage the Agile software delivery team to prioritize focus and minimize project switching. Emphasize the benefits of completing one task before moving on to the next, fostering a sense of accomplishment.
- Time Blocking:
- Introduce time-blocking techniques where team members dedicate specific time periods to focused work on a single project. This helps minimize interruptions and allows for more concentrated effort.
- Limiting Work in Progress (WIP):
- Apply the concept of limiting work in progress (WIP) in Agile methodologies. By restricting the number of tasks being actively worked on, teams can improve flow, reduce context-switching, and enhance overall efficiency.
- Prioritizing Backlog:
- Work with the team to prioritize the backlog and focus on the most critical tasks first. This ensures that attention is given to high-priority items before moving on to less critical ones.
- Encouraging Communication:
- Promote open communication within the team regarding workload and commitments. This helps in identifying potential bottlenecks or situations where individuals might be overburdened, allowing for adjustments.
The Law of Raspberry Jam is a concept closely associated with Gerald Weinberg’s broader insights into human behavior, software engineering, and consulting. Applying this concept can contribute to creating a more focused and efficient Agile software delivery environment.
References:
1. Gerald Weinberg (1991). “__title__”. Quality Software Management: Systems Thinking.
- “The Secrets of Consulting” by Gerald Weinberg:
- Weinberg’s book “The Secrets of Consulting” (1991- Quality Software Management: Systems Thinking) contains the Law of Raspberry Jam and provides insights into consulting principles, including considerations for project management and multitasking.
- Gerald Weinberg’s Writings:
- Explore other writings and articles by Gerald Weinberg, who was a prolific author in the fields of software engineering and consulting. His works often provide valuable perspectives on team dynamics and project management.
- Consulting and Project Management Books:
- Look for books on consulting and project management that reference or discuss the Law of Raspberry Jam. These books may provide practical applications and case studies.
Visit the Agile Coach’s Toolkit for more definitions, models, theorems and stuff.