What It Is:
The Cynefin framework is a sense-making framework developed by Dave Snowden. It helps individuals and teams make sense of complex problems and situations. The framework categorizes problems into five domains, each suggesting different approaches and strategies based on the nature of the problem. The domains are:
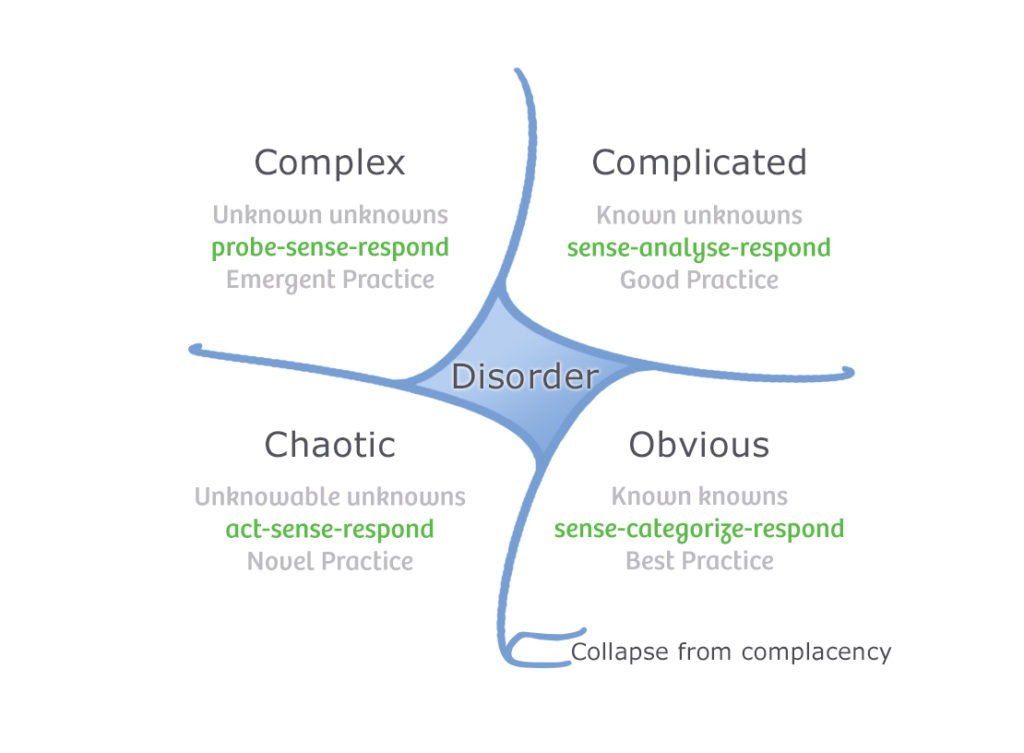
- Simple (Obvious) Domain:
- Characteristics: Clear cause-and-effect relationships, well-defined processes.
- Approach: Best practices and standard operating procedures work well.
- Complicated Domain:
- Characteristics: Multiple cause-and-effect relationships, experts can analyze and find solutions.
- Approach: Analyze, use experts, and apply good practices.
- Complex Domain:
- Characteristics: Cause-and-effect relationships are unclear, outcomes emerge through exploration.
- Approach: Probe, sense, respond; conduct experiments to learn and adapt.
- Chaotic Domain:
- Characteristics: No clear cause-and-effect relationships, requires immediate action to establish order.
- Approach: Act quickly to stabilize, then transition to the Complex or Complicated domain.
- Disorder Domain:
- Characteristics: When it’s unclear which domain a problem belongs to.
- Approach: Requires sense-making to determine the nature of the problem and then apply the appropriate approach.
 Using the Cynefin framework can help Agile teams navigate complex situations more effectively, make better decisions, and foster a culture of continuous learning and adaptation.
Using the Cynefin framework can help Agile teams navigate complex situations more effectively, make better decisions, and foster a culture of continuous learning and adaptation.
How to Use It:
Using Cynefin Framework in Agile Coaching:
- Problem-Solving Approach:
- Guide the team to identify the nature of the problem they are facing. Differentiate between simple, complicated, complex, and chaotic issues to determine the most effective approach.
- Decision-Making:
- Help the team understand the type of decision-making required in different domains. In the Simple domain, use known best practices; in the Complicated domain, rely on expertise; in the Complex domain, experiment and learn; in the Chaotic domain, act to establish order.
- Adaptation and Learning:
- Emphasize the importance of continuous adaptation and learning, especially in the Complex domain. Encourage the team to experiment, gather feedback, and adapt their strategies based on the emerging insights.
- Facilitating Retrospectives:
- Use the Cynefin framework as a tool during retrospectives to categorize challenges and identify appropriate actions. It helps teams reflect on how they approach problems and what strategies are most effective.
- Sense-Making:
- Train the team on sense-making techniques, especially in the face of uncertainty. Cynefin helps in making sense of complex situations by guiding teams on how to probe and respond.
References:
- “Cynefin: Weaving Sense-Making into the Fabric of Our World” by Dave Snowden:
- Dave Snowden’s foundational paper on the Cynefin framework provides an in-depth understanding of its principles and applications.
- Cynefin Framework Videos and Talks:
- Watch videos and talks by Dave Snowden or other experts explaining the Cynefin framework and its application in various contexts.
Use of Dave Snowden’s or Cognitive-Edge material does NOT imply and endorsement from Dave Snowden or Cognitive Edge. The Cognitive Edge method is ©2017 Cognitive Edge (USA) Inc., used with permission under a Creative Commons Attribution-Noncommercial-Noderivs license.
Visit the Agile Coach’s Toolkit for more definitions, models, theorems and stuff.