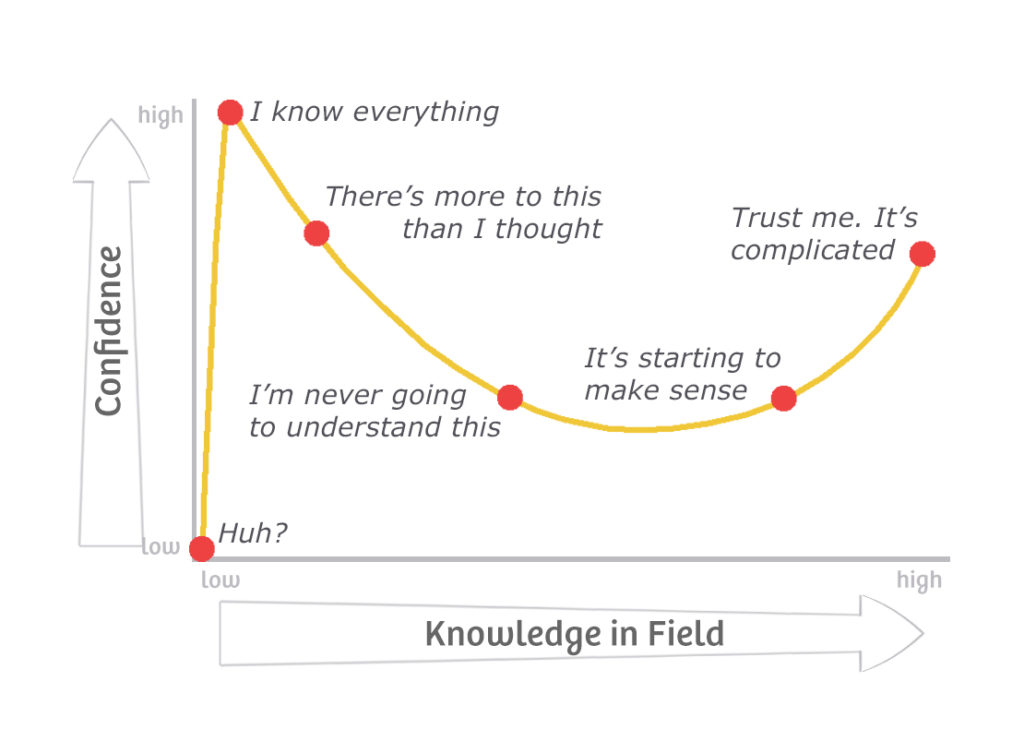
What It Is:
The Dunning-Kruger effect is a cognitive bias in which individuals with low ability at a task overestimate their ability. Essentially, it’s a phenomenon where people who are incompetent or have little expertise in a particular area tend to believe they are more competent than they actually are. On the other hand, those with high ability may underestimate their competence.
Origin of Dunning-Kruger Effect: The term “Dunning-Kruger effect” originated from a 1999 research paper titled “Unskilled and Unaware of It: How Difficulties in Recognizing One’s Own Incompetence Lead to Inflated Self-Assessments.” The paper was authored by psychologists David Dunning and Justin Kruger. In their study, Dunning and Kruger conducted a series of experiments that demonstrated this cognitive bias.
How to Use It:
Using Dunning-Kruger Effect in Agile Coaching:
- Self-Awareness Workshops:
- Incorporate discussions on the Dunning-Kruger effect in Agile coaching workshops. Help team members understand the importance of self-awareness and the potential impact of overestimating or underestimating their skills.
- Feedback Sessions:
- Encourage a culture of constructive feedback within the team. Provide regular feedback on individual and team performance to help team members gain a more accurate understanding of their competencies.
- Skill Assessments:
- Use skill assessments and self-assessment tools as part of professional development. This can help team members identify areas where they may be overestimating or underestimating their skills.
- Peer Reviews:
- Implement peer review processes where team members provide feedback to each other. Peer reviews can offer valuable insights and perspectives that individuals might miss due to the Dunning-Kruger effect.
- Continuous Learning:
- Emphasize the value of continuous learning. Create a learning culture where team members are encouraged to seek opportunities for skill development and growth.
Understanding the Dunning-Kruger effect can contribute to building a more realistic and self-aware Agile team. By addressing this cognitive bias, teams can foster an environment of continuous improvement and skill development.
References:
- Original Research Paper:
- Read the original research paper by Dunning and Kruger titled “Unskilled and Unaware of It.” It provides in-depth insights into the experiments conducted and their findings.
- David Dunning and Justin Kruger (1999). “Unskilled and Unaware of It: How Difficulties in Recognizing One’s Own Incompetence Lead to Inflated Self-Assessments”. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology. 77
- Read the original research paper by Dunning and Kruger titled “Unskilled and Unaware of It.” It provides in-depth insights into the experiments conducted and their findings.
- Books and Publications:
- Explore books and articles that discuss the Dunning-Kruger effect and its implications. Some psychology and behavioral science books delve into the concept and its relevance in various contexts.
- Psychology Journals:
- Consult psychology journals for additional research and studies related to the Dunning-Kruger effect. Journals often publish follow-up studies and analyses.
- Online Psychology Resources:
- Visit reputable psychology websites and resources that cover cognitive biases. These platforms may provide accessible explanations and real-world examples of the Dunning-Kruger effect.
Visit the Agile Coach’s Toolkit for more definitions, models, theorems and stuff.